Frequently asked questions
Answers about vehicle registration, tires, vehicle tax and more. Use the search or browse through our categories.


Vehicle registration document (registration certificate part I)
What do I need to know about my vehicle's registration certificate?
I lost my vehicle registration document - what now?
What are my obligations regarding my vehicle registration document?
Where was the cheat device installed? (Diesel scandal)
Tires
Tires (sizes, types, inches, properties)
How do I find the right tires for my vehicle?
Do tires always have to be expensive?
When should you change your tires?
Can tires be repaired?
Taxes
What is vehicle tax?
How does the vehicle tax system work?
Is vehicle tax mandatory?
How much is the vehicle tax for cars?
How much is the vehicle tax for motorcycles?
How much is the vehicle tax for trailers?
How much is the vehicle tax for motorhomes?
How much is the vehicle tax for trucks?
How much is the vehicle tax for electric vehicles?
How much is the vehicle tax for classic cars?
Can you save vehicle tax with seasonal plates?
What do I need to know about my vehicle's registration certificate?
The registration certificate consists of two parts: The first part is the vehicle registration document (Registration Certificate Part I). The second part is the vehicle title (Registration Certificate Part II). The vehicle title represents the operating permit and is issued for all vehicles requiring registration. It is mandatory for vehicle registration and deregistration. When purchasing a vehicle, you receive it from the dealer or previous owner. The vehicle title is a type of ownership certificate and does not need to be carried while driving. It should be kept in a safe place.
The following data is listed in the vehicle title:
- Technical data of the vehicle, such as the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN), engine displacement, engine power, weight, vehicle dimensions, number of axles and seats, as well as technical modifications to the vehicle.
- The name of the owner and, if applicable, previous owners
- Information about any deregistrations and re-registrations.
The registration office issues the vehicle registration document. Its content is very similar to the vehicle title and also contains all technical data about the vehicle as well as the name and address of the owner. Additionally, it contains the due date for the next vehicle inspection (MOT). You must always carry the vehicle registration document while driving to present it during traffic checks if required.
I lost my vehicle registration document - what now?
It's simple: Apply for a new one. But what do you need to apply for a new vehicle registration document and who do you contact? Before applying for a new vehicle registration document, you should first file a loss report with the local vehicle registration authority. This means contacting the authorities either by email or phone to report your vehicle documents as lost. If your vehicle registration document was stolen, you will additionally need a theft report from the police.
1. What do I need for the new application?
It's best to bring all documents for the application at once to save time. For applying for a new vehicle registration document, you need the following documents:
- ID card (or registration certificate or passport)
- Vehicle title / Registration Certificate Part 2
- Informal affidavit of loss (police theft number)
- MOT test report according to § 29 StVZO (proof of valid MOT)
If you no longer have the last test report at hand, Dekra or TÜV can also help in this situation. You can request a copy of the document there, usually informally by phone. However, if your car is new and has not yet undergone an MOT, this point is naturally omitted. You can also ask family members or friends to apply for the new vehicle registration document on your behalf. Remember to issue a power of attorney with your signature for this purpose.
What does a new application cost?
As you might expect: There are definitely fees for the new application. This depends on the respective federal state or authority. However, you can expect costs between 11 EUR and 50 EUR. It's best to take care of your vehicle registration document and not lose it in the first place. Additional costs may arise if the authority charges a fee for your loss report. If a notarized declaration of loss is required, it must be submitted to and certified by a notary. This can incur costs between 19 EUR and 27 EUR.
What are my obligations regarding my vehicle registration document?
Every vehicle owner is obligated to carry their driver's license while driving. Additionally, you are required to carry the vehicle registration document. It contains important information for the authorities. The forgery-proof document contains information about the name, first name, and address of the vehicle owner, as well as information about the brand, vehicle class, type, and structure of the vehicle. The curb weight and permissible total weight of your car also play an important role during checks.
1. What happens if I drive without the vehicle registration document?
As a driver, you are obligated to carry your vehicle registration document, as well as your driver's license. Occasionally, you might forget one of these documents and get checked. In that case, the trip costs not only fuel or electricity but also a fine. Driving without a registration document costs 20 EUR. Driving without a driver's license costs 30 EUR. So remember to always carry your documents with you.
2. Can I carry a copy of my vehicle registration document?
No. The Registration Certificate Part 1 is a forgery-proof document and therefore cannot be copied. Simple copies are not valid documents and will not protect you from fines.
3. What about a color copy?
Carrying a color copy of your vehicle registration document is not only wrong but also raises suspicion of document forgery. It is therefore not only inadvisable to carry a simple copy of your vehicle registration document, but especially prohibited to have or create a color copy.
4. Where should I keep my vehicle registration document?
In any case, you should have it with you when driving your vehicle. Where you store it plays an interesting role only for insurance reasons. If you place your vehicle registration document visibly, for example on the driver's seat, your insurance will judge differently in case of theft than if it's stored in the glove compartment. In any case, you should store your vehicle registration document in a non-visible place in the car. Ideally, place it where it's neither visible nor difficult to reach if you encounter a police check.
Where was the cheat device installed? (Diesel scandal)
The EA189 has been installed since 2007 in VW models Jetta, Golf, Beetle, Tiguan, and Passat. At Audi, almost all 1.2, 1.6, and 2.0 TDI engines with Euro5 classification have the EA 189 on board. The successor engine is also affected by the scandal. The EA288, as the successor model, is also at the center of the diesel scandal that became known in 2015.
1. Where was the EA288 installed?
Specifically, this concerns the EA288 engine series. These are the successor models to the EA189 engine, which was at the center of the diesel scandal that became known in 2015. The engine has been installed millions of times in VW Group diesel cars since 2012 - including in the Golf, Tiguan, or Passat. The EA288 engine was thus installed in many models from VW, Audi, Seat, and Skoda. Affected vehicles contain a 1.6 L or 2.0 L engine. It is now also clear that this engine contains an illegal defeat device, meaning significantly more cars are affected by the emissions scandal than previously assumed.
2. How do I find out if my car is affected?
It's important to know where you can check which vehicles are affected. You only need your car's chassis number or Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) and the respective manufacturer's websites. You can find this number in the vehicle documents and multiple times on the vehicle itself. Additionally, you can check whether the EA189 or EA288 engine was installed by checking the engine number. You can find the engine number directly on the engine itself, not in the vehicle registration document. The engine number is clearly stamped or milled into the engine. You can also find the engine number in the service booklet, as this number is necessary for ordering spare parts.
3. Who receives compensation?
The Federal Court of Justice has ruled on this: VW must pay damages. Due to intentional and immoral damage, the court decides that the car company must refund the purchase price minus usage compensation. However, the car must then be returned. In 2017, it became clear that VW must also pay compensation to its customers affected by the emissions scandal in Germany. In most cases, consumers receive the purchase price of the dirty diesel minus usage compensation plus interest. However, there are no class action lawsuits in Germany like in the US. All affected parties must individually sue for their rights and claims in court. It is therefore generally not possible for car owners to join a class action against VW. However, many lawyers have since offered consultation in such cases.
4. When do compensation claims expire?
Clarified for 2021: If a car buyer knew at the end of 2015, when the scandal became public, that their vehicle was affected, then their damage claim expired at the beginning of 2019. Diesel buyers asserting damage claims against VW must observe the three-year statute of limitations. A three-year limitation period according to § 199 Para. 1 BGB expires at the end of the year in which your claim arose and you as the affected party became aware of it. So if a claim becomes due on July 16, for example, the limitation period does not begin in July but only on December 31. Despite everything, since the beginning of 2020, there has been no compensation for models affected by the scandal.
Tires (sizes, types, inches, properties)
Tires are the only contact between the car and the road. They significantly influence a vehicle's driving behavior. They are specifically designed for surface conditions, temperature, and load. Theoretically, there is an optimally suited tire for every driving situation. Thus, various tire types are available on the market, manufactured for specific purposes. Considering production costs and tire lifespan, it's important to cover the broadest possible spectrum when purchasing a set of tires. For normal road traffic, for example, summer tires are produced for the warm season, winter tires for the cold season, all-season tires for all seasons, off-road tires for terrain use, or studded tires specifically for areas with icy road surfaces.
How do I find the right tires for my vehicle?
You can find the permissible tire size for your vehicle in your vehicle registration document under code "23". This usually indicates the optimal tire size, though in many cases multiple tire dimensions are allowed and approved for mounting. When you translate your vehicle registration document with us, we offer you a search assistant to avoid mistakes during research.
| Identifier ID | Speed | |
|---|---|---|
| Q | up to 160 km/h | |
| R | up to 170 km/h | |
| S | up to 180 km/h | |
| T | up to 190 km/h | |
| H | up to 210 km/h | |
| V | up to 240 km/h | |
| W | up to 270 km/h | |
| Y | up to 300 km/h | |
| ZR | over 240 km/h |
Do tires always have to be expensive?
Poor, old, or heavily worn tires can become a major safety hazard on the road. Since a tire's most important task is to maintain full contact with the road surface, if it fails to do this, expected driving behavior and safety are compromised. The decisive factors for choosing the right tire are both the car and its intended use. Generally, everyone is well advised to use season-appropriate tires. However, tires don't have to be expensive. Prices usually differ based on brands or tread patterns. Some tread structures contribute to improved road grip, which is especially advantageous for high-powered vehicles. However, there are no fixed list or base prices for any tire model. Each tire dealer negotiates their own terms with manufacturers individually. Whether price advantages are passed on to customers is also decided independently by each dealer. Our tip: Buy your tires counter-cyclically. Summer tires in winter and winter tires in summer. This way you're least likely to buy expensive tires. However, remember that mounting, balancing, and disposal of old tires incur additional costs.
When should you change your tires?
Once car tire tread depth falls below the 1.6mm minimum mark, you may no longer use them on public roads. The tires must be disposed of as they are no longer considered road-safe. If you're caught in a traffic check, you'll face a fine of 60 EUR plus one point in Flensburg. This is required by law. If the police determine you've endangered other road users or caused an accident, this fine increases to 75 or 90 EUR. When purchasing new car tires, their tread depth is usually between seven and nine millimeters. You can check this using a 1-euro coin, for example. The golden edge of the coin is exactly three millimeters wide. Without taking exact measurements, this allows you to estimate the tire's wear phase. For instance, if summer tires fall below three millimeters of tread depth, this already affects wet weather handling.
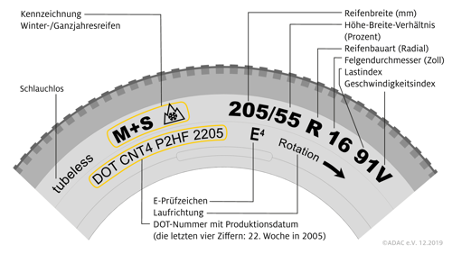
How to read tire markings: The marking 205/55 R 16 91V in our example means the following:
- The number at the beginning indicates the tire width in millimeters. Our example tire is "205" millimeters wide.
- The "/55" explains the aspect ratio of height to width of the tire cross-section in percent. A /50 would mean the tire is half as high as it is wide.
- R indicates the tire construction type: R stands for radial, today's standard tire construction.
- 16 indicates the rim diameter in inches on which the tire should be mounted.
- 91 is the load index for the car tire. 91 stands for 615 kilograms.
- The last position shows the speed symbol, indicating the tire's maximum permitted speed. V means a maximum speed of 240 km/h.
Issue: Tires can "age"
Even if the remaining tread depth is sufficient, very old tires can cause problems. This is due to the rubber compound, which begins to harden over time. In this case, grip and braking distance in wet conditions are negatively affected. This is particularly noticeable with winter tires, which must remain "soft" even at very low temperatures. Winter tires lose a crucial part of their properties after about six years. We therefore generally advise against using winter tires older than eight years. Summer tires, on the other hand, we recommend changing after eight to ten years. It's important to check the age of tires when purchasing summer or winter tires. Many tire formats may already be slightly aged due to systematic storage. There are age markings on delivered tires that can be checked. The production date is read on the tire's sidewall. There you'll find a so-called DOT number, which might read "1219" for example. This means the tire was produced in the 12th calendar week of 2019.
Can tires be repaired?
In short: Yes. However, it depends on the type of damage. If there are punctures in the tread area, for example from running over a nail, repairs can often be made. This is usually repaired using warm or hot vulcanization processes. However, some tire manufacturers generally exclude repairs. The decision to exclude tire repairs lies solely with the tire manufacturer.
What is vehicle tax?
The Federal Republic of Germany collects billions in vehicle taxes every year. These funds are essentially intended to fully refinance the expansion and maintenance of German road systems. The tax has been levied since the beginning of the 20th century. Previously, there was a so-called road usage fee, which was collected individually by municipalities. Now vehicle taxation is anchored in the Basic Law. The responsibility for tax administration lies with German Customs.
How does the vehicle tax system work?
To ensure all users contribute to financing the taxpayer-funded road infrastructure, there is a vehicle tax system. Essentially, it's about refinancing construction and maintenance through taxation of motorized vehicles. Initially, a tariff was calculated based on engine displacement and drive type. This meant that large and heavy vehicles should pay more vehicle tax as they fundamentally represent a greater burden on roads. Diesel engines are taxed highest compared to gasoline engines or electric vehicles. In 1985, legislators introduced emissions classes. Accordingly, vehicle tax rates today are based on the following criteria:
- Engine displacement
- Drive type
- Pollutant emissions and CO² output
- (Curb weight + maximum authorization)
Different tax rates also influence vehicle owners' purchasing behavior, acting as a political instrument. This allows legislators to steer market development in favor of environmentally friendly vehicles. For example, modern drives, especially electric motors, are promoted and taxed less. So when purchasing a new vehicle, always consider all costs. On Fahrzeugschein.de, you can easily check the current vehicle tax rate by scanning your vehicle registration document.
Is vehicle tax mandatory?
In short: Yes, of course. The obligation exists insofar as every motor vehicle owner must pay vehicle tax after it's levied. Vehicle trailers or owners of foreign vehicles are also subject to tax if they use their car in Germany more than temporarily. For cars from the European Union, the home country's registration certificate is sufficient. Other foreign drivers must carry an international registration certificate. Tax liability according to the Motor Vehicle Tax Act (Kraft-StG) begins with the vehicle's registration date, not with formal acquisition.
How much is the vehicle tax for cars?
By definition, it's a passenger car when at least 2 axles, an independent drive, and usually four wheels are used for passenger transport. For vehicles of this type used for passenger transport, the Federal Republic of Germany, German Customs, initially distinguishes between gasoline and diesel engines. For vehicle registrations before June 2009, emissions classes are additionally considered in relation to engine displacement for calculating vehicle tax.
Gasoline engines registered after June 2009 are taxed at 2.00 EUR per 100 cubic centimeters of displacement or part thereof. The tax rate for diesel engines has been 9.50 EUR per 100 cubic centimeters or part thereof since then. Additionally, emission values for cars are important for the calculation. The so-called base amount is tax-exempt.
- for first registration between July 1, 2009 and December 31, 2011: 120 g/km
- for first registration between January 1, 2012 and December 31, 2013: 110 g/km
- for first registration from January 1, 2014: 95 g/km
For vehicles first registered until the end of 2020, an additional 2.00 EUR is charged for each cubic centimeter per kilometer of CO² emissions . This is calculated regardless of whether a diesel or gasoline engine is installed. Legislators want to create greater incentives to establish low-emission vehicles. So from January 1, 2021, the principle applies: the higher the CO² emissions, the higher the tax. Since then, a graduated scale from level 1 to 6 applies. Starting at 2.00 EUR (95g - 115g/km) at level 1 and 4.00 EUR at level 6 (over 195g/km).
Calculation example
A car with a gasoline engine was first registered on March 6, 2012. The engine displacement is 1,420 cm³. The emission value is 135 g/km.
Tax calculation
1. Calculation of displacement-based tax
Per 100 cm³ of displacement or part thereof, the vehicle tax for a gasoline engine is 2.00 Euro. Therefore: 15 × 2.00 Euro = 30.00 Euro.
2. Calculation of CO₂-based tax
For a gasoline engine, the CO₂ emission-based vehicle tax is 2.00 Euro per g/km. After your car's first registration, 110 g CO₂ per km is tax-free as a base amount. Therefore, the exceeding 25 g/km must be multiplied by 2.00 Euro to get the tax portion for CO₂ emissions of 50.00 Euro.
3. Total vehicle tax
So the annual vehicle tax, possibly rounded down to full euros according to KraftStG, totals 80 EUR. Fahrzeugschein.de finds all relevant vehicle-related data for calculating your vehicle tax. Required are vehicle type, engine type (field P.3), displacement (field P.1), date of first registration (field B), and CO₂ emissions in g/km (field V.7).
How much is the vehicle tax for motorcycles?
In complete contrast to the car taxation system, light motorcycles with engine displacement under 125 cubic centimeters and maximum power up to 11 kW are completely tax-exempt. They are not taxed. Motorcycles with higher power values and larger displacement are taxed in a graduated scale. Emission values are not considered in the calculation. From 125 cubic centimeters, a vehicle tax of 1.84 EUR per 25 cubic centimeters or part thereof applies. Thus, the vehicle tax for a 750 cc motorcycle is calculated as 30 x 1.84 EUR = 55.20 EUR. Note that legislators only charge full amounts, so in this example a tax of 55 EUR would apply.
Although differences in motorcycle and car taxation are currently being discussed, a decision for legislative change is not foreseeable. It could lead to emission values being additionally included in future calculations. However, this would also result in changes to EU emission regulations, which complicates decisions about the legal situation.
How much is the vehicle tax for trailers?
Yes, trailers are also subject to tax liability under the law. Once trailers require registration, they are also subject to vehicle tax law. Trailers for agricultural and forestry use, as well as for transporting animals and equipment for sporting purposes, are exempt from registration. The tax is calculated at 7.46 EUR per 200kg of total weight or part thereof. However, the total tax is capped at 373.24 EUR. A truck owner can even be exempted from trailer tax. In this case, a corresponding surcharge would be added to the towing vehicle's tax, which is calculated based on the trailer's permissible total weight.
How much is the vehicle tax for motorhomes?
For calculating motorhome vehicle tax, both total mass and emissions class are considered. Motorhomes are designated as "special purpose vehicles" according to framework guidelines for motor vehicles and trailers, provided they contain certain equipment. This includes tables and seating, sleeping facilities, cooking facilities, and provisions for storing luggage and other materials. The basis for taxing motorhomes or caravans remains the Motor Vehicle Tax Act. Despite this, a separate vehicle class was introduced for motorhomes or caravans. Everyone knows the green and yellow badges. Despite having their own vehicle class, motorhomes are classified in the corresponding emissions classes (S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, EEV, Other). This is also the basis for determining motorhome tax. Additionally, consideration of the caravan's total weight is crucial for calculation. The calculation is graduated in 200kg increments.
How much is the vehicle tax for trucks?
In German usage, commercial vehicles are understood as trucks, lorries, or HGVs. They are used almost exclusively in road traffic for transporting various goods. Semi-trailers that can have trailers attached are included. A driver's license of class B, C1, or C enables driving such vehicles. License classes also differ in the permissible total weight to be moved. For an additional trailer weighing over 750kg, the driver needs an additional trailer license of class BE, C1E, or CE. Despite differences in weight classes, equally strict regulations apply to drivers, such as driving times and breaks.
- Small trucks up to 3.5 t
- Light trucks up to 7.5 t
- Medium-weight trucks up to 12t
- Heavy trucks with 40 t
Tractors are also tax-classified as trucks. They place particular strain on roads and the environment. Besides emissions and noise classes , permissible total weight is also relevant here. For exact tax calculation, a distinction is made between vehicles with total weight up to 3.5 tons and those with higher weight. Similar to motorhomes, we also move in 200kg increments starting at 6.42 EUR per 200kg or part thereof.
- Vehicles up to 2 tons = 11.25 EUR per 200kg or part thereof
- Vehicles from 2 to 3 tons = 12.02 EUR per 200kg or part thereof
- Vehicles from 3 to 3.5 tons = 12.78 EUR per 200kg or part thereof
Truck tax calculation example
Commercial vehicles are registered for a total weight of 4,500 kg and classified in emissions class 1. The mass of 4.5 tons corresponds to 23 started 200kg increments. Together with the emissions class, this results in the following tax rate:
| kg (200kg increments) | Tax rate | Total |
|---|---|---|
| 1-2000 (1-10) | 6,42 € | 64,20 € |
| 2001-3000 (11-15) | 6,88 € | 34,40 € |
| 3001-4000 (16-20) | 7,31 € | 36,55 € |
| 4001-4600 (21-23) | 7,75 € | 23,25 € |
Total 158.40 €
How much is the vehicle tax for electric vehicles?
Legislators aim to create a more environmentally friendly market situation through different taxation strategies for vehicles with combustion engines. Ultimately, it should make more economic sense for buyers to purchase vehicles with the lowest possible emissions class. Even though electric motors don't directly emit pollutants during operation, this drive type is also subject to vehicle tax. However, the tax calculation is reduced by around 50 percent compared to other drive types. This is intended to significantly promote the development of innovative electric vehicles. Basically, the same rules apply for alternative drives, only the amount of vehicle tax is halved.
How much is the vehicle tax for classic cars?
Historically valuable motor vehicles, so-called classic cars, are marked with an "H" suffix on the license plate. These vehicles can become real collector's items through extensive restoration measures and serve as a hobby for many car enthusiasts. Since well-maintained classic cars spend more time in the garage than on the road, there is a tax benefit here. If the traditional technology is in nearly original condition and is at least 30 years old, a tax benefit can be obtained through a technical assessment. Both maintenance and repairs must be done properly, with spare parts that corresponded to the technology of that time. For classic cars, a vehicle tax of 191.73 EUR is charged annually. Since October 2017, an application for seasonal plates for classic cars is even possible. In this case, tax is only due for those months when the vehicle can be driven.
Can you save vehicle tax with seasonal plates?
In short: Yes! A seasonal plate describes a time-limited registration of a vehicle. The vehicle tax is then only calculated for those months when the vehicle can be registered. Using the motor vehicle on public roads (including parking) is not allowed outside this time-limited registration. Consequently, the total vehicle tax will be lower than in a permanently registered state. In the case of seasonal plates, the Motor Vehicle Tax Act is not very extensive, but it still contains many regulations that apply and don't apply under different conditions.
Digital vehicle registration with many more features
Manage your vehicles digitally: Fuel log, MOT reminders, cost overview and more - all in one app.